Dear Readers BYD was founded in February 1995, According to BYD publications it is a high-tech multinational company devoted to leveraging technological innovations for a better life. After more than 29 years of high-speed growth, BYD has established over 30 industrial parks across 6 continents, China, the United States, Canada, Japan, Brazil, Hungary, and India and played a significant role in industries related to electronics, auto, renewable energy and rail transit. With a focus on energy acquisition, storage, and application, BYD offers comprehensive new energy solutions with zero-emission. BYD has expanded from 20 employees to around 290,000. BYD: short for Build Your Dreams.
Global warming,driven by increased concentrations of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide, poses significant threats to our planet. It leads to rising temperatures, which cause severe weather events, melting ice caps, rising sea levels, and disruption of ecosystems. These changes threaten biodiversity, agriculture, water supply, and human health, making global warming one of the most pressing environmental issues today.
The importance of addressing global warming cannot be overstated. If left unchecked, it could lead to catastrophic consequences, including more intense and frequent natural disasters, loss of habitable land due to sea-level rise, and severe impacts on food security and human health. Efforts to mitigate global warming are crucial to ensuring a stable and sustainable future for all life on Earth.
Solar energy and electric vehicles (EVs) are pivotal in the fight against global warming. Solar energy harnesses the power of the sun, providing a clean, renewable source of electricity without emitting greenhouse gases. By reducing reliance on fossil fuels, solar power helps decrease the overall carbon footprint. As solar technology advances, it becomes more efficient and affordable, making it a viable solution for reducing emissions on a large scale.
Electric vehicles also play a crucial role in mitigating global warming. Traditional internal combustion engine vehicles are significant contributors to greenhouse gas emissions. EVs, powered by electricity, produce zero tailpipe emissions. When charged with renewable energy sources like solar or wind power, the environmental benefits of EVs are maximized. This transition from fossil-fueled vehicles to electric ones is essential for reducing the transportation sector’s carbon emissions.
The combined use of solar energy and electric vehicles can significantly contribute to lowering global temperatures. By reducing dependence on fossil fuels and decreasing greenhouse gas emissions, these technologies help slow the rate of global warming. Moreover, their widespread adoption can lead to cleaner air, reduced pollution, and healthier ecosystems, ultimately creating a more sustainable and resilient planet. Through continued innovation and supportive policies, solar energy and EVs can be central to global efforts to combat climate change.
Strategy:
From launching the world’s first mass-produced PHEV model, the F3DM, in 2008 to rolling out 7+4 Full Market EV Strategy in 2015, BYD has always combined the goal of zero emissions with an understanding of market needs to fulfill its commitment to transforming transportation and eliminating fossil fuels.
Mission:
Technological innovations for a better life during the daytime, solar farms capture the power of sunshine;at night, energy storage systems deliver power to families.Electric vehicles on the streets and SkyRail systems along green beltsconnect the city with zero emissions and zero pollution & to provide more possibilities for a better life. Observing a new energy future approaching.This is the mission of BYD, and the green dream of all mankind.
Industries Engagement:
The company has diversified into areas such as cellphone assembly and solar cell manufacturing.
BYD has four industries dedicated to realizing its green dreams of creating a zero-emission energy ecosystem: automobile, electronics, new energy, and rail transit. BYD is listed on the Stock Exchange in both Shenzhen and Hong Kong, China.
BYD is also a pioneer in battery technology. After its successes with manufacturing batteries for mobile telephones and laptops, BYD decided to create a complete clean-energy ecosystem that reduces the world’s reliance on fossil fuels. BYD is dedicated to making mobility solutions emission-free.
In the past decades BYD has focused on mastering advanced technologies, power batteries, electric motors, electronic control systems and semiconductor chips. BYD offers electric trucks, electric busses, electric forklifts and even electric rail solutions. The company has become the world’s leading manufacturer of new energy vehicles (NEVs), exceeding more than 200,000 sales per month.
BYD entered the European market with three all-new pure-electric passenger cars. At the Paris Motor Show in October 2022, BYD unveiled its innovative and technologically-advanced electric car range to customers in Europe. This includes the BYD ATTO 3, an expressive and dynamic C-segment SUV, designed with the European customer in mind, as well asl the BYD TANG, which is a 7-seater with variable all-wheel drive. We also presented the sleek and sporty BYD HAN, an E-segment saloon.
BYD a high-tech brand.
BYD is not just a car manufacturer. Emerging from this considerable R&D the company developed the ground-breaking Blade Battery. This battery pack is revolutionizing safety, durability and performance in the EV industry. The Blade Battery works in close synergy with BYD’s exceptional competency in electric powertrain technology for the ultimate in system efficiency and integrated vehicle intelligence. Combined, this integrated technology has been developed to deliver optimum performance and a better driving experience. Notably, BYD owns the entire vertical supply chain for seamless integration and total manufacturing control, including the production of semiconductors.
Driving this innovation in technology, is a sincere commitment from BYD to provide safe and appealing solutions that reduce pollution from carbon emissions and address the issue of climate change, supporting the initiative to Cool the Earth by 1℃. The green dream has long been a priority for BYD and is the vision for the future.
For over two decades, BYD has been at the forefront of sustainable innovation. In 2008, BYD launched the world’s first mass-produced plug-in hybrid vehicle F3DM at the Geneva Motor Show. BYD was also the first automotive OEM in the world to announce it would be ceasing production of ICE vehicles to focus on BEV and PHEV products. BYD is the first, and only company in the world, to provide full market new energy vehicle solutions.
Global leader in new energy vehicles.
BYD is the global leader in NEVs and the third largest automotive brand in the world, based on market capitalization. BYD has ranked as number one for sales of NEVs in China for nine consecutive years. BYD is a true explorer when it comes to cleaner energy and has major aspirations for the future. This joins seamlessly perfect with the mobility goals of its automotive partners in Europe.
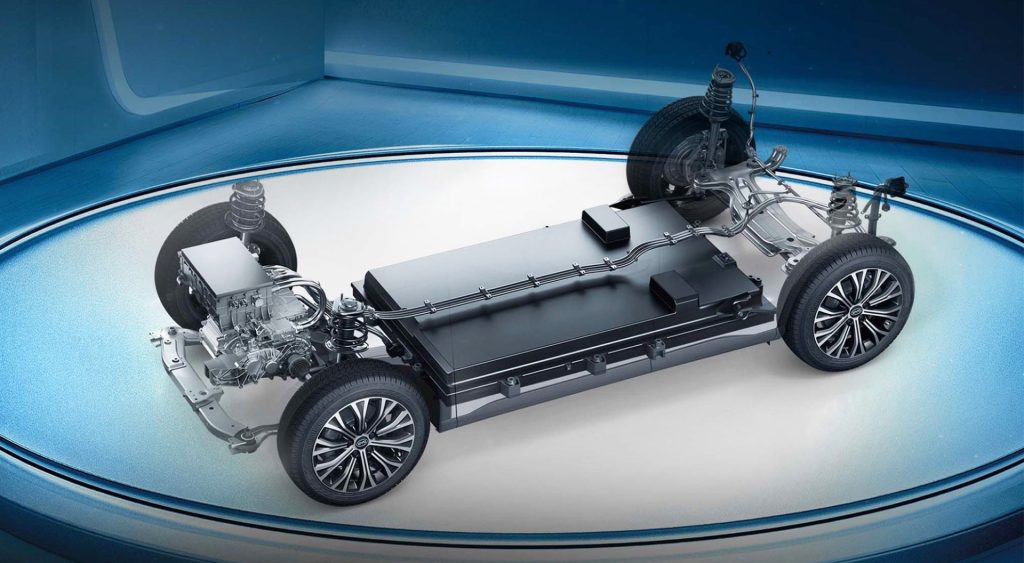
BYD has developed the industry-leading Blade Battery, e-Platform 3.0 and Dual-mode hybrid power technology accelerating the once-in-a-century transition from fossil fuel powered vehicles to electric vehicles.
Written by Aqeel Bashir & this exclusive article has been published in Automark Magazine’s June-2024 printed edition too.